| TSP Lab
| GPRS monitoring system
| Sga-GPRS
|
SGA-GPRS
Table of contents
Introduction
Goals
- Monitoring GPRS links for GPRS messages and creating traffic statistics from them
- Monitoring SS7 (Gn interface between the sGSN and the HLR) and GTP (Gn interface between the SGSN and the UGSN) links
looking for deciphering information (if ciphering is turned on)
- Customizability; reliability; scalability
- Cell related statistics can be created
- Providing GPRS statistics for the operator's Performance Management System (PMS)
- Remote maintaining of the components
Operating principles
- Connecting to the operator’s Gb and HLR links
- Collecting and assembling GPRS messages from the monitored network
- Monitoring SS7 and GTP messages for dechipering
- After deciphering GPRS messages are stored in a circular buffer
- GPRS statistics are calculated and sent from the monitors to the server
- Statistics about dechipering are created with adjustable periodicity
- A remote client (which can be either the server or an other computer) can request the GPRS messages and can decode them
Miscellaneous functions
- Alarms are sent to network operator’s NOC by SNMP traps or sent by SMS's
- Adjustable log detail levels from ‘Off’ to ‘Debug’
System Architecture
The topology of a system is depicted in the figure below.
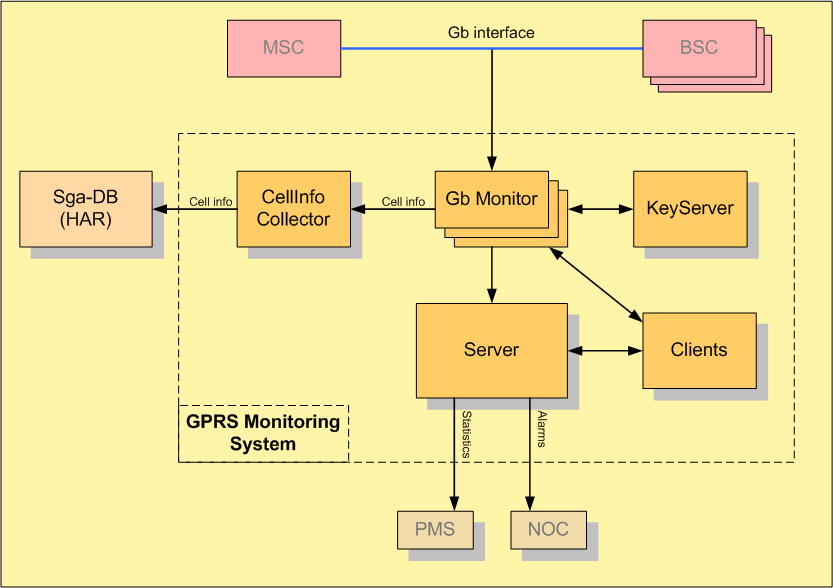
The components of the Sga-GPRS system are
- the Gb monitoring units, simply referred to as "Monitors", which are connected to the
- the Key-Server unit, consisting of
- GrMonitor, connecting to the Gr links and the GPRS KeyServer
- GTPMonitor, connecting to the Gn links and the GPRS KeyServer
- GPRSKeyServer, connecting to the GrMonitor, the GTPMonitor and the GPRSMonitors
- the Sga-GPRS server, which is connected to the

